MODIS and VIIRS Instruments
Although quite similar in their design and capabilities there are significant differences between the two sensors that can and do result in differences in their products.
| Instrument | MODIS (Aqua) | VIIRS |
|---|---|---|
| Orbital Altitude | 705 Km | 824 Km |
| Equatorial Crossing Time | 13:30 Local Time | 13:30 Local Time |
| Measurement Swath Width | 2330 Km | 3040 Km |
| Nadir Pixel Size (primary retrieval band) | 1.0 Km | 0.75 Km |
| Swath Edge Pixel Size | 2 Km | 1.5 Km |
| Spectral Bands Used for Retrieval |
0.44, 0.55, 0.65, 0.86 1.24, 1.38, 1.63 and 2.11 microns |
0.49, 0.55, 0.67, 0.86 1.24, 1.38, 1.61 and 2.25 microns |
The picture below shows a comparison of a one day global retrieval of MODIS and VIIRS.
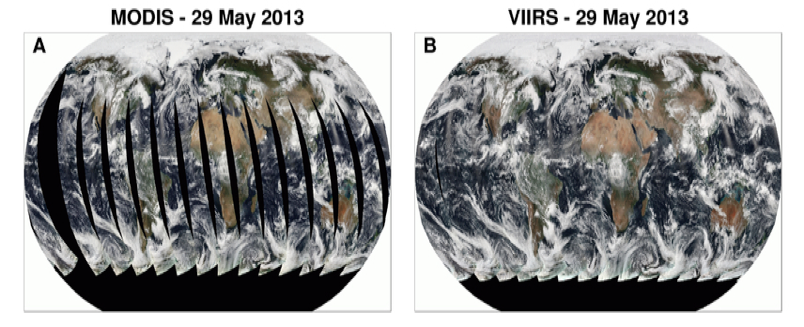
Figure 1. One day global retrieval true color image from MODIS (A) and VIIRS (B). Note that MODIS has gaps near the equator. VIIRS has a wider swath width which eliminates these gaps.
The table below summarizes some of the product differences between MODIS and VIIRS some of which are consequences of the different sensor capabilities and orbit. Other differences have to do with product creation choices and/or algorithm changes. These will be explained in more detail in the rest of the guide.
| Sensor | MODIS (Aqua) | VIIRS |
| Nadir Product Size | 10 x 10 Km | 6 x 6 Km |
| Number of pixels aggregated for product | 100 1 Km pixels | 64 0.75 Km pixels |
| Granule Size | 5 Minutes; 203 x 135 pixels | 6 minutes; 404 x 400 pixels |
| File Format | HDF4 | netCDF-4 |
![]()
Figure 2. Product Sizes: At left: MODIS 10×10 km level 2 pixel retrieved from 1×1 km level 1b pixels, compared to the size of the VIIRS level 2 product size in lighter blue. At right: VIIRS 6×6km product retrieved from 0.75×0.75 km level 1b pixels.
